Valve d'équilibrage LoadMatch™ avec évent à raccorder au drain

Ces valves douées d'auto-tarage sont des équilibrages qui combinent des fonctions additionnelles en une seule cartouche: passage libre en sens inverse, limitation de la pression liée à la charge, limitation de la pression due à la dilatation thermique. Le clapet permet un passage libre depuis le distributeur (orifice 2) vers la charge (orifice 1), alors qu'une fonction de pilotage à action directe tare automatiquement la valve à environ 1,3 fois la pression induite par la charge, jusqu'au tarage de la pression du limiteur thermique. Une contrepression sur l'orifice 2 n'altère pas les performances de l'auto-tarage car la chambre du ressort est référencée a un drain (à l'orifice 4).
- Le dispositif de régulation de la valve LoadMatch™ permet au tarage de s'ajuster en dynamique, en réponse aux variations de la pression induite par la charge, alors que le limiteur de la pression thermique est actif à un tarage fixe. Cette régulation génère un tarage dynamique inférieur au tarage du limiteur thermique, sans jamais dépasser le nécessaire, en préservant la sécurité et la fiabilité du contrôle de la charge. Aussi, tant que le tarage dynamique est inférieur au tarage thermique, la pression de pilotage requise pour ouvrir la valve est généralement inférieure aux autres valves de contrôle, à tarage égal du limiteur thermique
- Dans la plupart des conditions de charge la régulation LoadMatch™ requiert une pression de pilotage inférieure aux autres valves d'équilibrage, à tarage égal du limiteur thermique.
- Avec la régulation LoadMatch™ les pressions de pilotage sont pratiquement identiques quelles que soient les pressions induites par la charge dans la plage opérationnelle.
- Toutes les valves à 4 orifices, équilibrage, contrôle de charge, et clapet piloté à l'ouverture, sont physiquement interchangeables (c.-à-d. même fonction pour chacun des 4 orifices, et même cavité pour une taille donnée). Note: Le six-pans de serrage de ces valves est plus large que celui des autres valves utilisant la même cavité, et cette différence doit être prise en considération pour les applications existantes.
- Corrosion resistant cartridge valves are intended for use in corrosive environments and are identified by the model code suffix /AP for external stainless steel components, or /LH for external zinc-nickel plated components. See the CONFIGURATION section for all options. For further details, please see the Materials of Construction page located under TECH RESOURCES.
- This valve is functionally a 4-port counterbalance valve. It seats as a poppet and modulates over a long stroke.
- Avec la plage de tarage G, le maximum recommandé pour la pression engendrée par la charge est de 319 bar (4625 psi). La pression d'ouverture la plus élevée avec la plage de tarage G sera de 400-438 bar (5800-6350 psi)
- Avec la plage de tarage H, le maximum recommandé pour la pression engendrée par la charge est de 212 bar (3075 psi). La pression d'ouverture la plus élevée avec la plage de tarage H sera de 265-293 bar (3850-4250 psi)
- Avec la plage de tarage J, le maximum recommandé pour la pression engendrée par la charge est de 265 bar (3850 psi). La pression d'ouverture la plus élevée avec la plage de tarage J sera de 331-365 bar (4800-5300 psi)
- Pour les versions LoadMatch™ la différence (en %) entre la pression d’ouverture et la pression de fermeture de la valve est identique. La tolérance sur le tarage est telle que notée.
- Les cartouches de maintien de charge et les équilibrages SUN peuvent être installées directement dans une cavité usinée dans le corps d’un récepteur pour renforcer la protection et améliorer la raideur du circuit.
- Cette valve possède des joints d’étanchéité entre tous les orifices.
- Cette valve a la pleine capacité en limitation de pression
- Cette valve intègre le concept Sun de la cartouche à visser "flottante" qui permet de minimiser les contraintes internes dues à un couple de serrage excessif de la cartouche et/ou à des écarts d’usinage des cavités ou des cartouches.
| Cavité | T-21A |
| Taille | 1 |
| Capacité | 15 gpm60 L/min. |
| Pression maximale de fonctionnement | 5000 psi350 bar |
| Pression Maximale Induite par la Charge Recommandée | Voir les Caractéristiques TechniquesVoir les Caractéristiques Techniques |
| Tarage en usine établi à | 2 in³/min.30 cc/min. |
| Fuite Maximale à la Fermeture | 5 drops/min.0,3 cc/min. |
| Pression d'ouverture du clapet de by-pass | 25 psi1,7 bar |
| Fermeture | ≥77% of setting≥77% of setting |
| Dimensions du six pans de la valve | 1,00 in.25,4 mm |
| Couple de serrage de la valve | 30 à 35 lbf ft41 - 47 Nm |
| Seal kit - Cartridge | Buna: 990021007 |
| Seal kit - Cartridge | Polyurethane: 990021002 |
| Seal kit - Cartridge | Viton: 990021006 |
Sun defines the setting of a counterbalance valve as the pressure at which it cracks open as a relief valve. The flow rate at "crack" is the point where drops turn to a stream, about 1-2 cubic inches per minute. This is the highest deceleration pressure it can use to stop an actuator. The valve should be set at least 1.3 times the maximum expected load-induced pressure at port 1. In many cases the maximum load-induced pressure will be the same as the system relief setting.
Three-port vented, or atmospherically referenced, counterbalance valves are considered problem solvers for existing circuits that used a three port, non-vented valve. If a vented valve is required in a new design, four-port valves are recommended. Atmospherically referenced valves, over time, will leak externally or allow moisture into the spring chamber (resulting in corrosion) even though the spring chamber is sealed.
Generally, the 25 psi check spring is recommended for most applications as it is more robust and insensitive to rapid flow reversals. The 4 psi check cracking pressure should be used if there is a need to pull in make-up oil.
We do not recommend it. There is a possibility that the pilot area could get filled with oil and slow down or prevent the closing of the valve. A correct solution is to connect port 3, the pilot port, to port 2, the outlet port.
Backpressure at port 2 (inlet) may adversely effect the operation of a three port counterbalance valve as it directly opposes pilot pressure. When backpressure exceeds pilot pressure, it adds to the setting of the valve at a rate of 1 plus the pilot ratio times the backpressure, i.e. with 200 psi (14bar) back pressure at port 2 on a 3:1 counterbalance valve, the setting would increase by 800 psi (55 bar). In effect, backpressure drives the counterbalance valve closed. Using vented counterbalance valves typically will correct this problem.
The vast majority of counterbalance applications are satisfied with a 3:1 pilot ratio. Lower pilot ratios will increase system stability and higher ratios will be more efficient. 10:1 pilot ratio valves generally should be avoided.
There are 2 styles of load-reactive counterbalance cartridge valves. The first was designed by Racine and has the pilot in port 1 or the nose of the cartridge. The second style that Sun adapted was conceived by Fluid Controls, and has the load port (port 1) at the nose and the pilot coming in port 3. Sun co-founder John Allen said that a counterbalance was a valve designed around a spring. For a given size of cartridge you design a spring that has the most force and rate that can be wound, and then design the rest of the valve. The spring force dictates the relief area needed to achieve a setting.
The Racine design has 2 diameters. There is a pilot diameter and a larger diameter that creates the annular relief area. In order to maintain capacity the larger diameter has to be as large as possible. In order to increase pressure settings the annular relief area needs to be reduced. Because the big diameter is fixed and the differential annular area is being reduced, the result is the pilot diameter increases; hence the high pilot ratios.
Sun's (Fluid Control's) design has 3 diameters, the small one and the middle one defining the relief area and the middle one and the large one defining the pilot area. This design gives us the freedom to create pilot ratios that fit the application.
No. The counterbalance will be less violent than the check valve but the flow dynamics create backpressure spikes that can damage the valve. The circuit needs to be designed to dissipate the energy in a controlled fashion.
Vented counterbalance valves should be used if you have backpressure in port 2 (inlet). Typical applications are regeneration circuits, master-slave circuits and servo/proportional valve circuits.
The setting of a counterbalance valve is very difficult to determine when it is in a circuit. This is due to cross-piloting, load-induced pressure, and cylinder ratio. The best way to check the setting is to remove the valve from the circuit. Before removing any valve, ensure machines and loads are mechanically held in position and that the valve is not under pressure at the time of its removal. Screw the valve into a simple, single cavity, line mounted body. Port 1 should be connected to a pressure source and ports 2 & 3 should be open. Increase the pressure on port 1 until the valve just starts to open. Repeat several times to ensure consistency.
The 5 drops/min. are at the point of reseat which is 85% of cracking pressure. If the valve is set correctly it will never see a load that is higher than 77% of cracking (1/1.3). At this pressure in a typical system the counterbalance can be considered a zero leak device. Using counterbalance valves to prevent drift is an accepted and common practice on almost all manlifts and hydraulically operated cranes. If a load drifts because of the counterbalance valve, the seat has probably been damaged and the valve should be replaced.
While cylinder drifting is often attributed to a leaking or damaged counterbalance valve, it can also be caused by cylinder seal leakage or changes in oil temperature. If you believe the seat of the counterbalance valve has been damaged, which can be caused by shock or contamination, it is advisable to replace the valve with a new factory set valve. Always follow the manufacturer's recommendations for servicing of hydraulically actuated machinery, and insure all loads are mechanically supported and cartridges are not under pressure when removed.
Il y a exactement 15 gouttes Sun dans un centimètre cube.
Yes it is sealed; however every time the valve is cycled a small amount of oil passes into the spring chamber--about 1 drop for every 4000 cycles. If the vent is blocked, the spring chamber will eventually fill with oil, building pressure until the valve won't open.
Counterbalance valves are pressure dependent devices, not flow dependent. They are designed to create pressure drop for their operation, so it is important not to oversize them. A higher pressure drop will generate greater system stiffness and help improve stability.
Two areas work to open a counterbalance valve, the relief area and the pilot area; the pilot area divided by the relief area equals the pilot ratio. Reverse flow from port 1 to port 2 is blocked by the check valve until a pilot pressure is sensed at port 3 (pilot) that is inversely proportional to the load pressure at port 1 (load). The pilot pressure at port 3 effectively reduces the relief valve setting. The setting is reduced according to the ratio of the differential pilot area on the piston compared to the differential relief area. For example, in a valve with a 3:1 pilot ratio, set for 3000 psi with a load of 2000 psi, the pilot pressure required to open the relief valve is 333 psi, i.e. (3000 psi - 2000 psi)/3 = 333 psi pilot pressure.
To calculate the pressure required to lower a load, use the following equations. These equations are under ideal conditions and do not consider any backpressure in the circuit or any effects of temperature on the oil.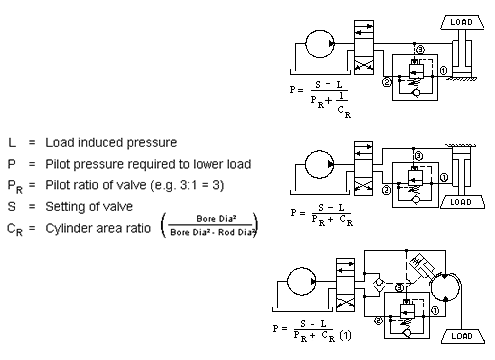
Hysteresis is the difference between the pressure at which the valve will crack open and then reseat closed. Sun's counterbalance valve's hysteresis is typically less than 15%, which means the valve will have reseated to a closed position at 85% of its cracking or opening pressure.
It is always recommended that a counterbalance valve be set before it is installed in an application. Correctly setting a counterbalance when it is installed is very difficult due to the pilot assist and the interaction with the actuator. Once installed the adjust screw should be considered a manual override.
A closed loop transmission is meant to transfer the energy from dynamic braking to the prime mover. A counterbalance valve would put the energy in the form of heat into the small amount of oil contained in the loop. Backpressure caused by dynamic braking from the pump and charge pressure complicate matters. "Putting a vented counterbalance in a closed loop transmission is a crime; putting a non-vented valve in is a felony; putting a 10:1 valve in is a capital offence." Jeff Baker
First the valve is set to just crack open at the desired setting. The pressure is dropped to zero and then brought up to 85% of the setting. The valve is then piloted open and allowed to reseat. At this point the leakage rate must be less than 5 drops per minute. One detail that makes this test critical is extremely clean oil. If a valve leaks in an application, the seat has probably been damaged by contamination and the valve should be replaced. Before removing any valve, ensure machines and loads are mechanically held in position and that the valve is not under pressure at the time of its removal.
- Cartouches Sun avec joints EPDM
- Sun Economise l’Energie grâce à la Technologie LoadMatch™
- Encore Une Solution Optimisée par Sun Hydraulics !
- Conseils Techniques pour les Valves d'Équilibrage et les Clapets Anti-Retour Pilotés
- Nouvel outil de sélection d’équilibrage QuickSelect LoadHolding
- À la Poursuite de la Valve d’Equilibrage Parfaite
- Les Equilibrages SUN LoadMatchTM Economisent l’Energie!
- Sun Étend ses Solutions Anticorrosion
- Nouvelle Séries Électrovannes & Bobines Sun FLeX ™
- QuickDesign with SmartConnect Offers Drag-and-Drop Schematic Tool
- Les cartouches de la taille 4 PLUS offrent un débit supérieur pour des pertes de charge inférieures
- Choosing Counterbalance Valves
- LoadAdaptive™ & LoadMatch™ Cartridges (713.18 Ko)
- Usiner les Cavités pour Cartouches Sun (521.84 Ko)
- Valves d'Équilibrage et Clapets Anti-Retour Pilotés (870.71 Ko)
- Performances et Caractéristiques Générales
- LES CARTOUCHES à VISSER SUN à “NEZ FLOTTANT” (447.56 Ko)
- Sun Model Code Explanation; 999-901-334 (343.9 Ko)
- Liste et Définition des Tailles de Cartouche et des Cavités SUN
- A Guide to Sun's Counterbalance Families
- Cartouches: Matières Utilisées dans les Produits SUN
- Recommandations pour les Fluides et les Températures
- Units of Measure, Settings, and Conversions
- Counterbalance Quick Reference (93.57 Ko)


